Industrial Evaporation Systems: Improving Process Efficiency and Resource Recovery
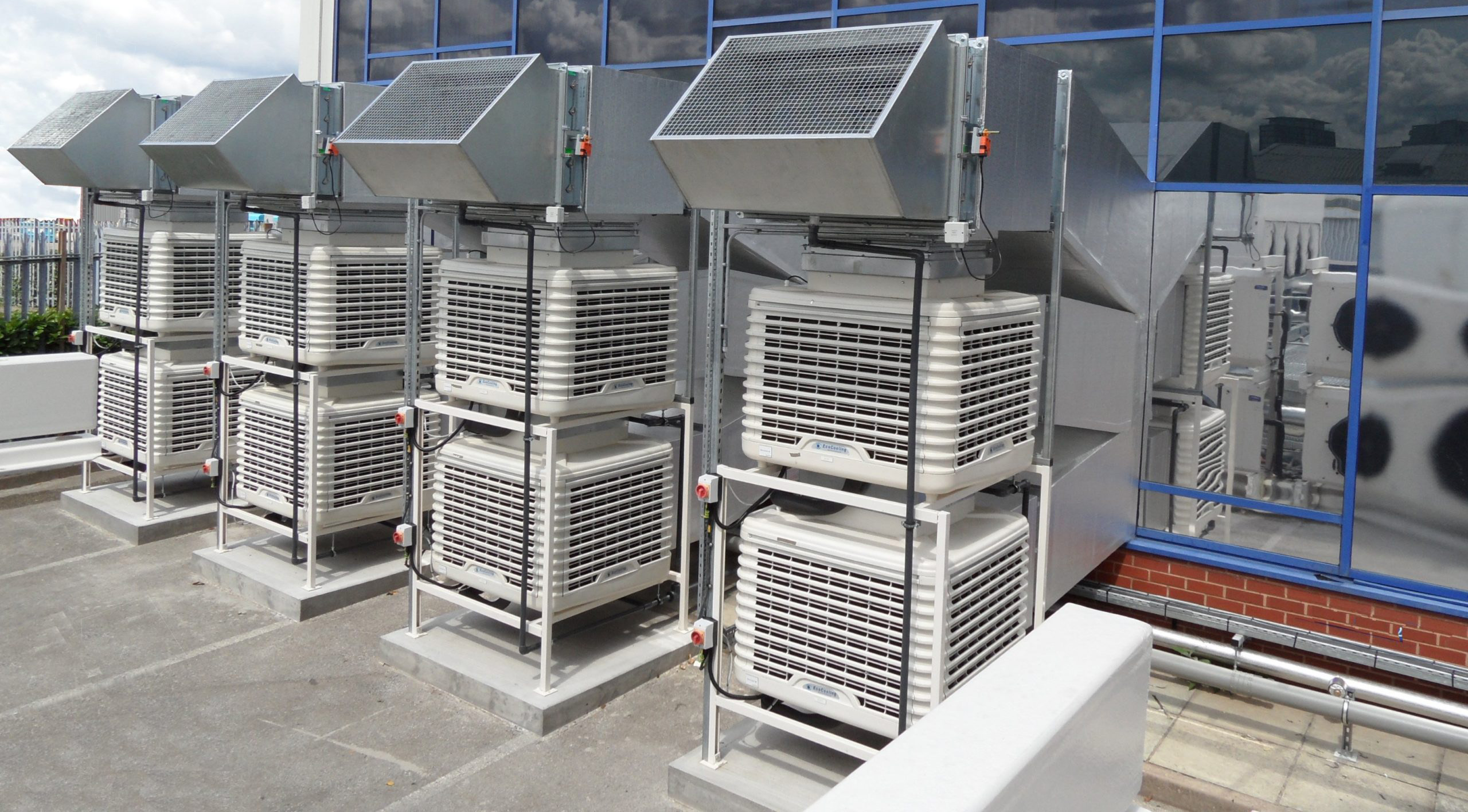
Industrial evaporation systems are essential equipment in the chemical industry, food processing and various other industries where concentration, separation and solvent recovery are critical processes. These systems, which include evaporators, distillation units and falling film evaporators, play a key role in optimizing production efficiency, reducing waste and recovering valuable resources. In this article, we will look at the different types of industrial evaporation systems and their applications in various industrial processes.
1. Evaporators:
Evaporators are widely used in industries such as food and beverage manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, and wastewater treatment to concentrate solutions by removing water through evaporation. These systems use thermal energy to evaporate the solvent, leaving behind a concentrated solution or solid residue. Key features and benefits of vaporizers include:
- Multiple Configurations: Evaporators are available in a variety of configurations, including falling film, forced circulation, and multi-effect evaporators, providing flexibility in design and operation to suit specific process requirements.
- Energy efficiency: Evaporators can be designed with energy-saving features such as heat exchangers, steam recompression, and thermal steam reuse to minimize energy consumption and operating costs.
- High Concentration Efficiency: Evaporators are capable of achieving high levels of concentration, making them ideal for processing heat-sensitive materials, extracting valuable products from dilute solutions, and reducing the cost of transporting liquid products.
- Versatile Applications: Evaporators are used in a wide range of industries, including milk processing, sugar processing, chemical synthesis and wastewater treatment, to concentrate liquids, separate components and recover solvents.
- Customizable Design: Evaporators can be customized with features such as corrosion-resistant materials, automatic control systems, and clean-in-place (CIP) systems to ensure reliable operation and meet industry standards.
2. Distillation units:
Distillation units are important equipment for separating the components of a liquid mixture based on differences in boiling points. These systems work by heating a mixture to create steam, which then condenses back into liquid form and is collected into separate fractions. Key features and benefits of distillation units include:
- High Separation Efficiency: Distillation units provide high separation efficiency to purify solvents, recover valuable chemicals, and produce high-purity products in industries such as petrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and beverage distillation.
- Scalability: Distillation units can be scaled up or down to suit varying production volumes and process requirements, making them suitable for both laboratory research and large-scale industrial production.
- Fractional Distillation: Advanced distillation technologies such as fractional distillation and rectification allow components with similar boiling points to be accurately separated, ensuring high purity and quality of the product.
- Process Optimization: Distillation units can be integrated with process control systems, reflux systems, and column internals to optimize separation efficiency, reduce energy consumption, and minimize product loss.
- Safety Features: Distillation units are equipped with safety features such as pressure relief valves, temperature sensors and emergency shutdown systems to prevent accidents and ensure operator safety during operation.
3. Falling film evaporators:
Falling film evaporators are specialized evaporation systems used to process heat-sensitive materials and viscous liquids. These systems work by allowing a feed liquid to flow in a thin film over the inside of vertical tubes while steam or hot gas is passed through the tubes to produce heat for evaporation. Key features and benefits of falling film evaporators include:
- Gentle Processing: Falling film evaporators provide gentle processing conditions with short dwell times and low operating temperatures, minimizing thermal degradation of sensitive materials and maintaining product quality.
- High heat transfer efficiency: The thin film liquid flow and turbulent vapor flow of falling film evaporators provide high heat transfer coefficients, allowing efficient evaporation and concentration of the feed liquid.
- Low fouling: Falling film evaporators are less susceptible to fouling than other types of evaporators due to the constant renewal of the liquid film and the self-cleaning action of the steam flow, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
- Compact Design: Falling film evaporators have a compact design and small footprint, making them suitable for installation in space-constrained environments and retrofitting existing production facilities.
- Flexible Operation: Falling film evaporators can operate under vacuum or atmospheric pressure conditions, providing flexibility in process control and optimization based on product requirements and energy availability.
Conclusion:
Industrial evaporation systems, including evaporators, distillation units and falling film evaporators, are essential equipment in a variety of industrial solvent concentration, separation and recovery processes. By harnessing the capabilities and benefits of these advanced evaporation technologies, businesses can improve production efficiency, reduce environmental impact, and achieve sustainable resource management. With ongoing advances in design, automation and process integration, industrial evaporation systems continue to play a vital role in driving innovation and progress across a variety of industries.