Title: Disclosure: Studying Laboratory Equipment in Clinical Settings
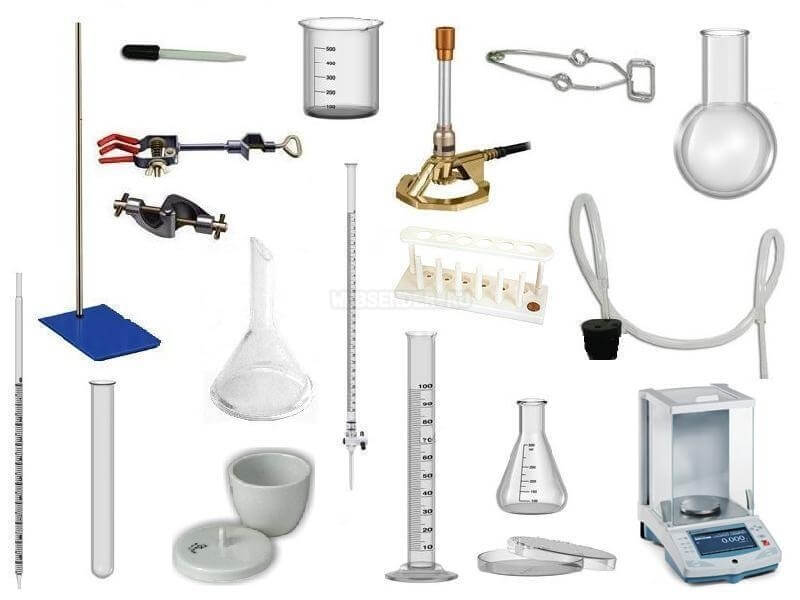
Introduction: Laboratory equipment forms the basis of clinical diagnosis and research, facilitating sample processing, testing and analysis to obtain vital information about patient health and disease conditions. From centrifuges and microscopes to analyzers and incubators, these instruments enable healthcare professionals to perform a wide range of diagnostic tests and experiments with high precision. In this study, we will take a closer look at the various types of laboratory equipment commonly found in clinical laboratories and dispensaries, their functionality and application in healthcare settings.
-
Centrifuges: Centrifuges are important laboratory instruments used to separate the components of a liquid mixture based on density and particle size using centrifugal force. These devices spin samples at high speeds, causing heavier particles to settle to the bottom of the tube while lighter components rise to the top. Centrifuges are used for a variety of purposes in clinical laboratories, including separation of blood components (such as plasma and serum), isolation of cells, and purification of nucleic acids and proteins for molecular diagnostics and research. They are available in a variety of types, including benchtop centrifuges, microcentrifuges, and refrigerated centrifuges, to suit a variety of laboratory needs.
-
Microscopes: Microscopes are optical instruments that magnify and visualize specimens at the microscopic level, allowing detailed examination of cells, tissues, and microorganisms. These instruments play a critical role in pathology, hematology, microbiology and histology laboratories for diagnostic and research purposes. Microscopes are available in a variety of configurations, including compound microscopes, stereo microscopes, and fluorescence microscopes, each suited to a specific application. They are used to analyze blood smears, examine tissue sections, identify pathogens, and conduct cell culture studies, among other tasks that help diagnose and monitor various diseases.
-
Analyzers: Analyzers are automated laboratory instruments designed to perform quantitative analysis of biological samples such as blood, urine and tissue fluids for diagnostic purposes. These devices use advanced technologies, including spectrophotometry, immunoassays and chromatography, to measure the concentrations of analytes such as glucose, cholesterol, electrolytes and hormones. Analyzers play an important role in clinical chemistry, hematology, immunology and microbiology laboratories, providing fast and accurate results for patient care and disease management. They streamline laboratory workflows, increase efficiency, and provide standardized testing protocols, facilitating high-quality care.
-
Incubators: Incubators are temperature-controlled chambers used to grow and maintain cell cultures, microorganisms, and other biological specimens under controlled environmental conditions. These devices provide a stable and sterile environment with controlled temperature, humidity and CO2 levels to support cell proliferation, differentiation and experimental conditions. Incubators are indispensable in cell culture laboratories, microbiology laboratories, and molecular biology laboratories for a variety of applications, including cell culture experiments, microbial growth studies, and enzymatic assays. They improve reproducibility, minimize contamination risks, and optimize experimental conditions for reliable research results.
Conclusion: Laboratory equipment serves as the cornerstone of clinical diagnosis and research, allowing healthcare professionals to perform a wide range of tests and experiments with accuracy and efficiency. Centrifuges, microscopes, analyzers and incubators are just a few examples of the diverse range of instruments used in clinical laboratories and dispensaries. Through the use of advanced technology and adherence to strict quality standards, laboratory equipment facilitates accurate diagnosis, disease monitoring and research advancements, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes. As technology advances, laboratory equipment will play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of medicine and scientific discovery.