Understanding Canine Body Language: What Your Dog Is Trying to Tell You
Interpreting your dog's body language is key to understanding his feelings, needs and overall well-being. Dogs communicate primarily through their posture, facial expressions, and vocalizations. Here are some general clues to help you decipher what your dog is trying to tell you:
1. Tail Wag:

Contrary to popular belief, a wagging tail does not always mean a dog is happy. The position and speed of the wobble can convey different emotions. A high, fast wobble often indicates excitement, while a low, slow wobble can signal uncertainty or caution.
2. Ears:

The position and movement of your dog's ears can give away his emotional state. Ears that are forward or erect usually indicate alertness or curiosity. Ears laid back may indicate fear, submissiveness, or discomfort.
3. Eyes:

A dog's eyes can tell a lot about his emotions. Wide eyes with dilated pupils may indicate fear or anxiety. Soft, relaxed eyes usually mean your dog is calm and content. Staring can be a sign of aggression or challenge.
4. Mouth and lips:
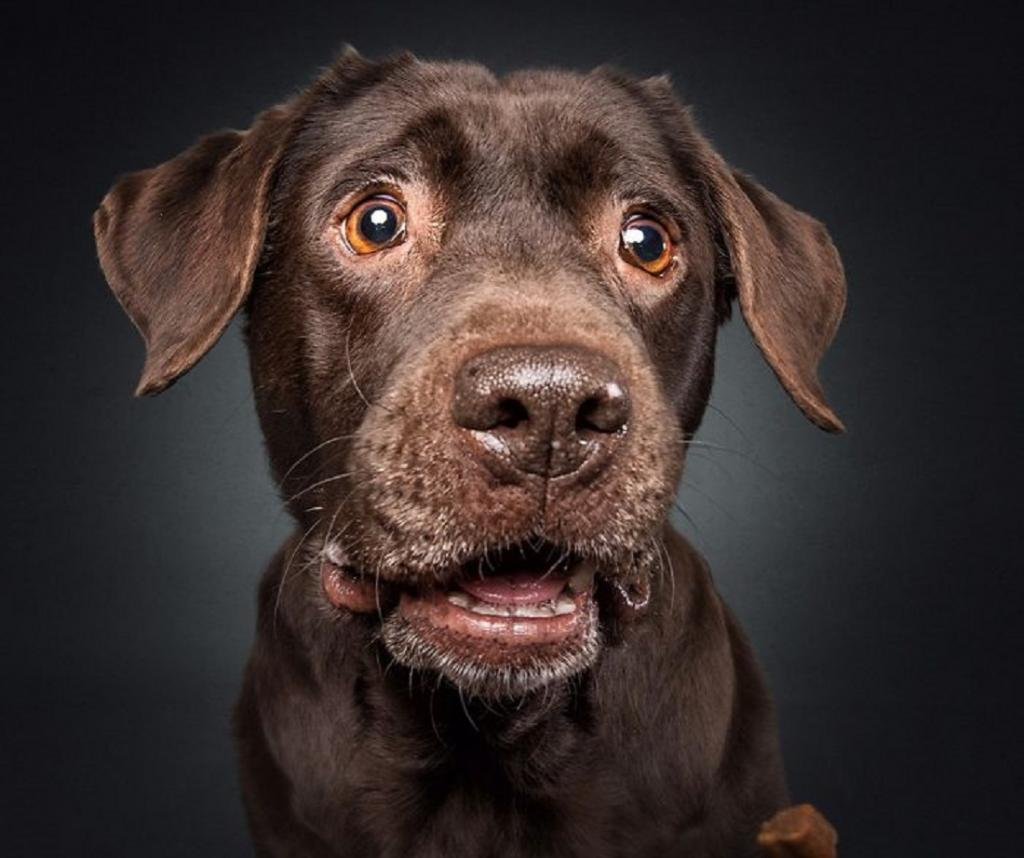

A relaxed, slightly open mouth with a protruding tongue is a sign of comfort. Licking your lips or showing your teeth without growling can be a sign of anxiety or stress. Yawning, especially when not tired, can also indicate stress or anxiety.
5. Body Pose:
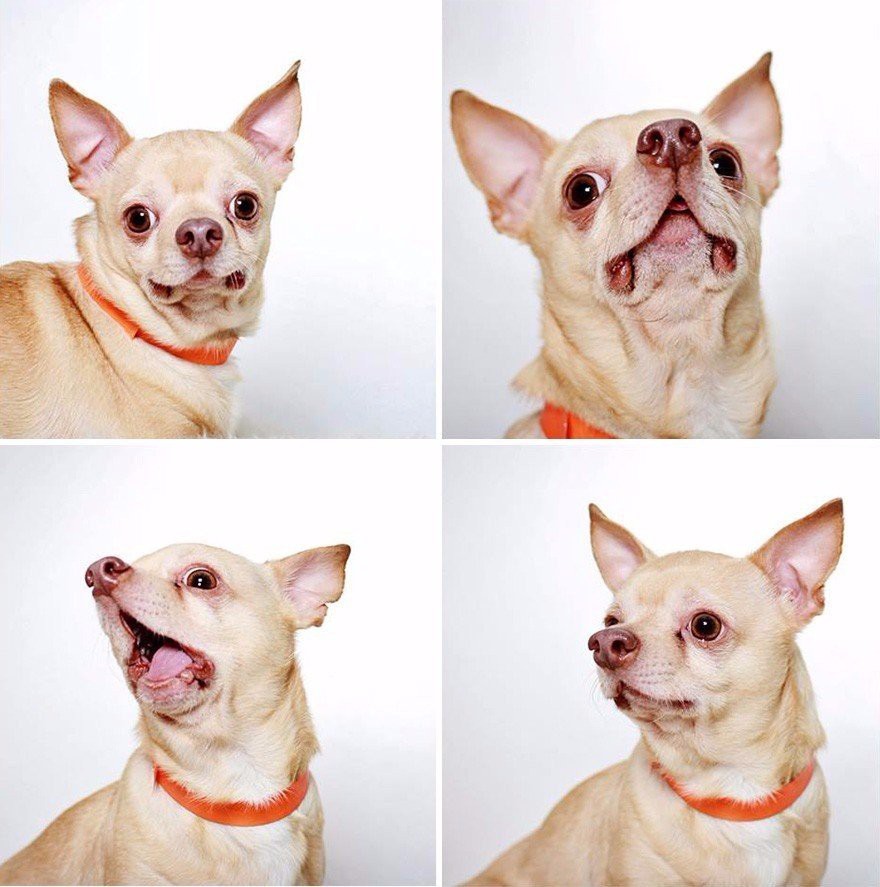

The general posture of the dog speaks volumes. A relaxed, relaxed posture with a wagging tail usually indicates a happy, confident dog. Stiffness, raised fur along the back and a tense body suggest agitation, fear or a readiness for aggression.
6. Vocalizations:
Dogs use different sounds to communicate. Barking, growling, whining or whining can convey different emotions. For example, a deep, continuous bark may signal alertness or warning, while a high-pitched whine may indicate excitement or distress.
7. Context and environment:
Pay attention to the context in which your dog exhibits certain behaviors. For example, a tucked tail, flattened ears, and cowering may indicate fear or submission, especially in unfamiliar or stressful situations.
8. Consistency and individuality:
Remember that every dog is unique and their body language can vary depending on breed, personality and past experiences. Understanding your dog's typical behavior patterns and reactions will help you interpret his signals more accurately over time.
Conclusion
By observing and interpreting your dog's body language you can deepen your bond and better meet his needs. Paying attention to subtle cues helps you respond appropriately and provide comfort or reassurance when needed. Paying attention to how your dog communicates improves communication between you and strengthens your relationship, leading to a happier, healthier life together.