Booster Car Seat Basics: Transitioning to Booster Car Seats for School-Age Children
As children grow and reach school age, their car seat needs change, requiring an upgrade to booster seats for optimal safety and comfort while traveling. In this article, we'll dive into the basics of using booster seats and discuss why they are necessary for school-age children, highlighting key considerations parents should keep in mind during this transition.
1. Purpose of booster seats:
Booster seats are designed to lift children to the correct height and position in the car seat while ensuring that the seat belt is properly secured to the chest and knees. This ensures that the seat belt is secured to the strongest parts of the child's body, such as the shoulder and pelvic bones, reducing the risk of injury in the event of a crash. Booster car seats provide additional support and protection for school-age children who have outgrown their forward-facing car seats but are not yet tall enough to use the car's seat belt alone.
2. Age and size requirements:
The transition to a booster car seat usually occurs when a child outgrows their forward-facing car seat, usually between the ages of 4 and 8, depending on their height, weight and developmental stage. It is important to check the booster seat manufacturer's height and weight limits to ensure it is appropriate for your child's size and age. Most booster seats are designed for children weighing more than 40 pounds and at least 4 feet 9 inches tall, although different models vary.
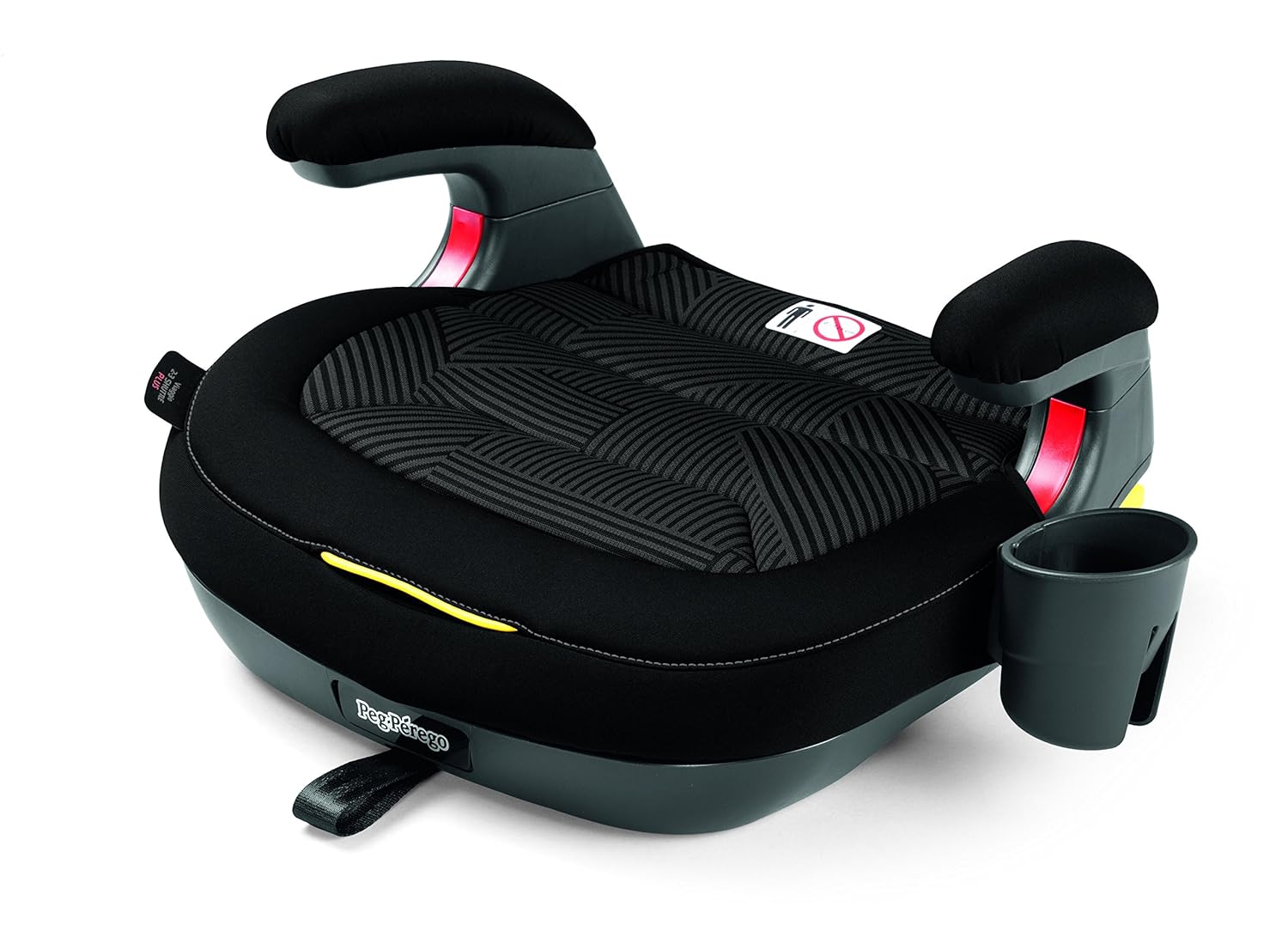
3. Types of booster seats:
There are two main types of booster seats: high-back and backless. High back booster seats provide extra support and protection for your child's head and neck, making them ideal for cars with low seat backs or no headrests. Backless booster seats are more compact and suitable for older children who no longer need additional head support. Both types of booster seats are designed to lift children to the correct height for proper seat belt installation and provide comparable safety benefits.
4. Correct placement of seat belts:
Proper seat belt placement is critical when using a booster seat to ensure maximum safety for school-age children. The shoulder strap should fit snugly across the child's shoulder and chest, without crossing the neck or slipping off the shoulder. The lap seat belt should fit snugly across the child's hips, not the stomach. Some booster seats have belt guides or clips to help parents and children fit the seat belt correctly.
5. Security Compliance:
When choosing a booster seat for your school-age child, look for models that meet or exceed safety standards set by regulatory organizations such as the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) or the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP). Look for seats with features like side impact protection, energy-absorbing foam, and secure mounting mechanisms to provide maximum protection in the event of a crash.
6. Gradual transition and constant monitoring:
It is important to take a gradual approach to the transition to a booster car seat and monitor your child's comfort and safety throughout the process. Start by using the booster seat for short trips and gradually increase the duration as your child gets used to the new seating arrangement. Monitor your child's behavior at all times and ensure they remain properly seated and restrained while using a booster seat to ensure maximum safety on the road.
In conclusion, upgrading to a booster seat is an important step in keeping school-aged children safe and comfortable while traveling in the car. By understanding the purpose of booster seats, age and size requirements, types of booster seats, proper seat belt placement, compliance with safety standards, and the importance of gradual transition and ongoing monitoring, parents can make informed decisions and ensure their children travel safely in the car.{ 45}