Overclocking Your Desktop: Pros and Cons
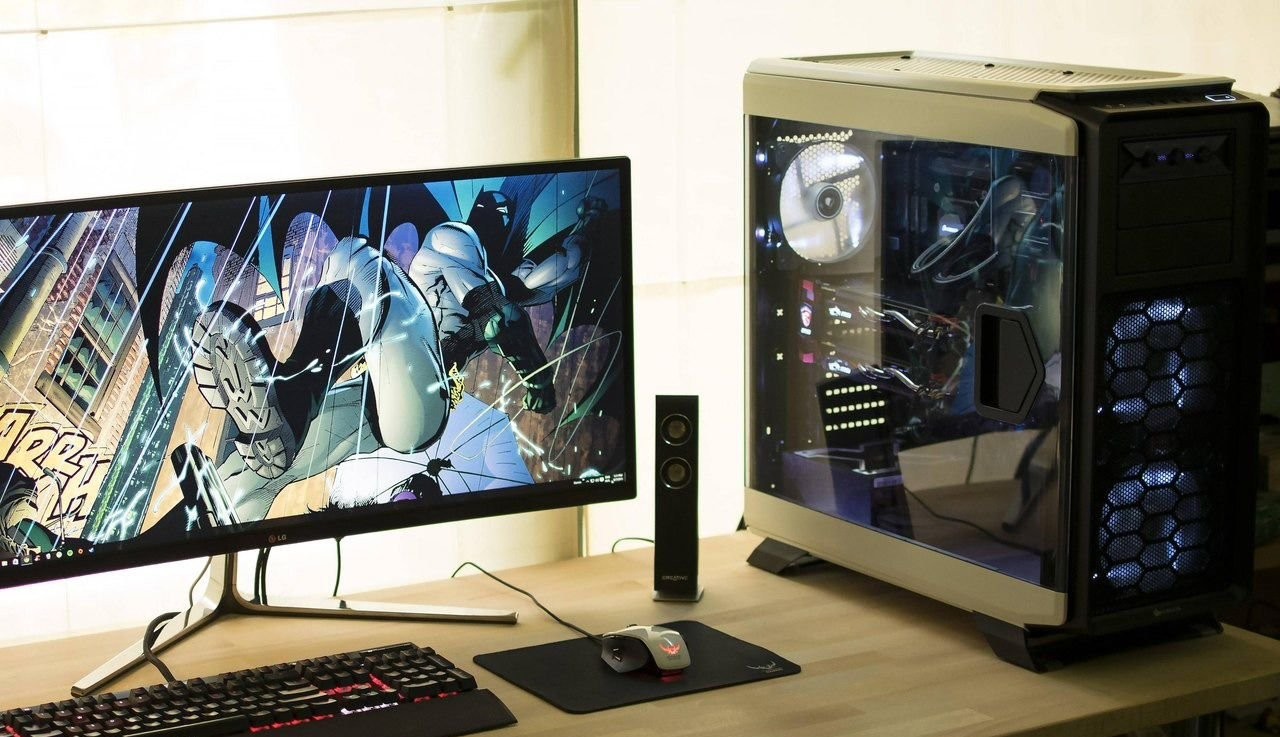
Overclocking is the practice of increasing the clock speed or multiplier of your desktop computer's CPU, GPU, or RAM to make them run faster than their factory specifications. While overclocking can provide performance gains, it also comes with certain risks and disadvantages. In this article, we'll look at the pros and cons of overclocking your desktop computer.
Pros of overclocking:
-
{eleven}
-
Cost Savings: Instead of purchasing more expensive, high-performance components, overclocking allows you to squeeze more performance out of your existing hardware, potentially saving money.
-
Extended Hardware Life: When done correctly and within safe limits, overclocking can extend the life of your components, keeping them competitive with newer hardware.
-
Tuning: Overclocking provides the flexibility to fine-tune your system's performance to suit your specific needs and preferences.
Improved performance: Overclocking can result in significant performance gains for tasks that require higher clock speeds, such as gaming, video editing, and 3D rendering.
Disadvantages of overclocking:
-
Stability Issues: Overclocking can make your system unstable, causing crashes, freezes, or data corruption if not done carefully.
-
Heat Dissipation: Overclocked components generate more heat, which can cause overheating and potentially damage your hardware if you do not use proper cooling solutions.
-
Voiding Warranties: Many manufacturers will void warranties if they discover that a component has been overclocked, leaving you responsible for any repair or replacement costs.
-
Reduced component life: Overclocking places stress on your components, potentially shortening their lifespan, especially if they are constantly running at high clock speeds.
-
Data Loss Risk: Unstable overclocking can result in data loss or corruption, so regular backups are necessary when overclocking.
-
Difficulty: Overclocking requires technical knowledge and careful monitoring of system parameters, which can be difficult for inexperienced users.
Safe overclocking tips:
If you decide to overclock your desktop computer, follow these tips to minimize the risks:
-
Research: Understand the capabilities and limitations of your hardware before attempting overclocking.
-
Use trusted tools: Use proven overclocking or BIOS tweaking software provided by your motherboard manufacturer.
-
Keep an eye on temperatures: Closely monitor component temperatures and invest in effective cooling solutions such as aftermarket CPU coolers or additional case fans.
-
Incremental changes:Increase clock speeds or multipliers gradually, checking stability after each adjustment.
-
Stress Testing: Use stress testing software to test the stability of your overclock and make sure it can handle long-term stress.
-
Data Backup: Back up your data regularly to protect against potential data loss due to instability.
-
Be aware of the warranties: Be aware that overclocking may void warranties, so consider the consequences before proceeding.
Conclusion:
Overclocking your desktop computer can be a useful way to gain additional performance, but it comes with risks that must be carefully managed. Whether you decide to overclock or not, it's important to prioritize system stability and ensure your hardware remains within safe operating parameters to avoid potential damage or data loss.