Motherboard Heatsinks and Cooling Solutions: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction: Motherboard heatsinks and cooling solutions play a critical role in maintaining optimal temperatures and ensuring stable system performance. In this comprehensive guide, we'll look at different cooling options, including heatsinks, and their importance in cooling your motherboard.
1. Need for cooling solutions:
- Modern CPUs, GPUs, and motherboards generate heat during operation that must be dissipated to prevent overheating.
- Efficient cooling solutions improve system stability, durability, and performance.
2. Radiators in liquid cooling systems:
- Headsinks are integral components of liquid cooling systems, including all-in-one (AIO) and custom water cooling systems.
- They consist of a series of tubes and fins through which coolant flows, removing heat using fans.
3. Air Cooling Solutions:
- Air cooling solutions typically consist of radiators and fans.
- They draw heat away from motherboard components such as the CPU and VRMS and dissipate it into the surrounding air.
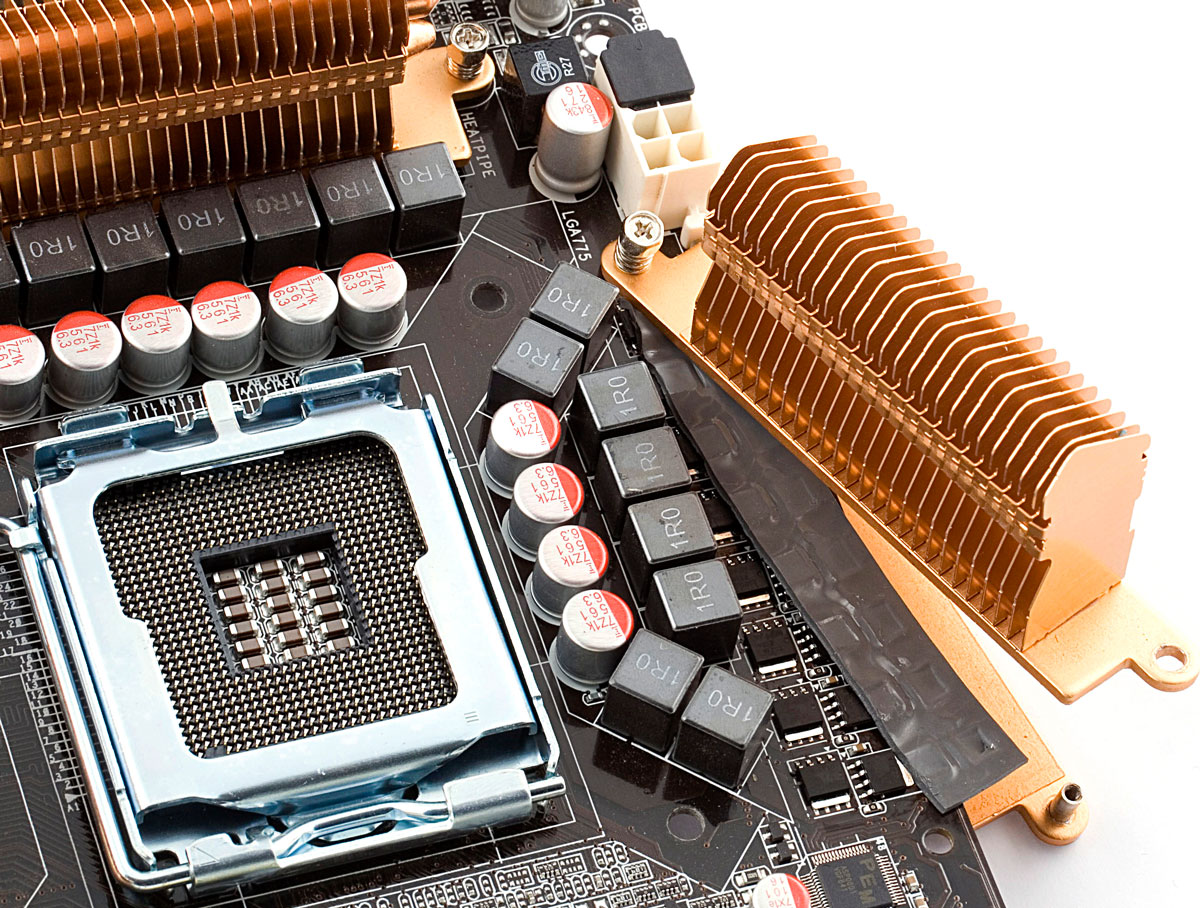
4. VRM cooling:
- Voltage regulator modules (VRMs) on motherboards require cooling to maintain stable power supply.
- Heatsinks and VRM fans are common features on high-end motherboards.
5. Chipset cooling:
- Chipsets on motherboards can generate heat, especially on high-end systems.
- Chipset heatsinks, often connected to a VRM cooling system, help dissipate heat efficiently.
6. Motherboard form factors and cooling:
- Smaller form factor motherboards (such as Mini-ITX) may have limited cooling space.
- When choosing cooling solutions, consider the motherboard form factor and case compatibility.
7. Radiator dimensions:
- The size of the radiator affects the cooling efficiency. Large radiators provide more surface area for heat dissipation.
- Compatibility of the heatsink with your PC case is very important.
8. Liquid Cooling vs Air Cooling:
- Liquid cooling solutions are generally more efficient, but can be more expensive and require maintenance.
- Air cooling solutions are simple, cost-effective and maintenance-free, but can be more cumbersome.
9. Overclocking and Cooling:
- Overclocked systems generate more heat and require robust cooling solutions.
- Enthusiast motherboards often feature advanced cooling capabilities for overclockers.
10. Cooling System Maintenance: - Regularly clean fans and heat sinks of dust and debris to maintain optimal cooling performance. - On liquid cooling systems, check the coolant level and for leaks.
11. Monitoring and Control Software: - Many motherboards come with software utilities to monitor and regulate fan speed and temperature. - Adjustable fan curves optimize cooling while minimizing noise.
12. Cooling Aesthetics: - RGB lighting options are available for cooling systems to customize the aesthetics of your system.
Conclusion: Effective cooling solutions, including heat sinks and heatsinks, are essential to keep the motherboard and component temperatures within safe limits. When choosing cooling options, consider your system usage, overclocking requirements, motherboard form factor, and case compatibility. Choosing the right motherboard heatsinks not only ensures stability, but also extends the life of your components, promoting a reliable and efficient PC setup.